-
Research Article
-
Development of a Landslide Susceptibility Map for Natural Slopes in the Busan Area Using Logistic Regression Model
로지스틱 회귀모델을 이용한 부산지역 자연사면의 산사태 예측지도 작성
-
Young-Suk Song, Kyeong-Su Kim, Hyun-Ju Oh
송영석, 김경수, 오현주
- In this study, a landslide susceptibility map was produced using a logistic regression model to predict the probability of landslide occurrences across …
본 연구에서는 부산지역 주요 자연사면을 대상으로 산사태 발생 가능성을 예측하기 위해 로지스틱 회귀모델을 이용한 산사태 예측지도를 작성하였다. 연구지역은 백양산, 황령산, 장산 및 …
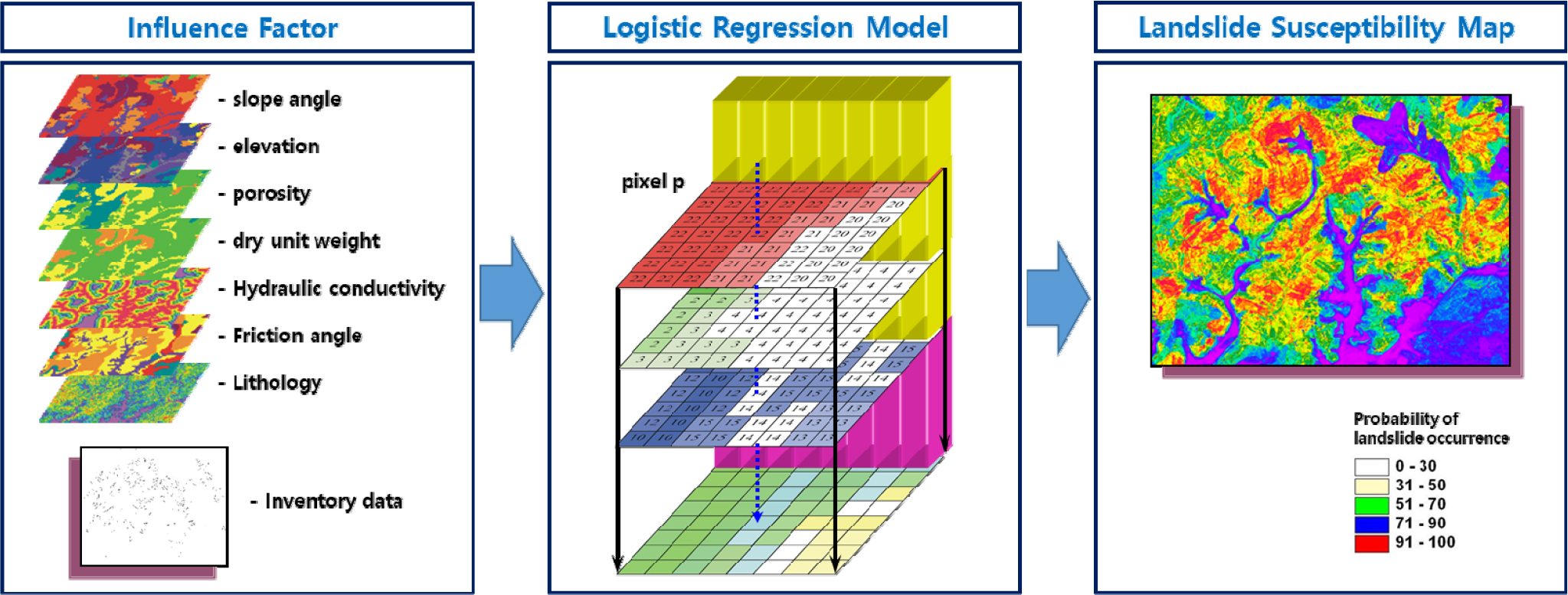
- In this study, a landslide susceptibility map was produced using a logistic regression model to predict the probability of landslide occurrences across major natural slopes in the Busan area. The study area was selected to include Mt. Baekyang, Mt. Hwangnyeong, Mt. Jang and Mt. Gudeok. A logistic regression model was employed to estimate the probability of landslide occurrence based on geological conditions. The geological and topographical characteristics of each area were investigated, and geotechnical properties such as void ratio, dry unit weight, hydraulic conductivity, and internal friction angle were determined. The collected data were then converted into spatial distribution maps using GIS techniques, which were then used to construct the landslide susceptibility map. The results showed that there are some high-risk zones where the probability of landslide occurrence exceeds 70%. In particular, the Mt. Gudeok area exhibited relatively wide zones with a high probability of landslides, whereas in the Mt. Baekyang, Mt. Hwangnyeong and Mt. Jang areas, only localized sections were identified as highly susceptible to landslides. The landslide susceptibility map developed in this study is expected to serve as fundamental data for landslide disaster mitigation and the establishment of disaster prevention measures in the Busan area.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 부산지역 주요 자연사면을 대상으로 산사태 발생 가능성을 예측하기 위해 로지스틱 회귀모델을 이용한 산사태 예측지도를 작성하였다. 연구지역은 백양산, 황령산, 장산 및 구덕산 일대로 선정하였으며, 로지스틱 회귀모델은 지질조건에 따라 산사태 발생 가능성을 산정할 수 있는 모델을 적용하였다. 이를 위해 각 지역의 지질 및 지형 특성을 조사하고, 간극비, 건조단위중량, 투수계수, 내부마찰각 등 지반공학적 특성을 산정하였다. 수집된 자료를 이용하여 GIS 기법을 통해 공간적 분포지도로 변환하였으며, 이를 기반으로 산사태 예측지도를 작성하였다. 산사태 예측지도 작성 결과 산사태 발생확률이 70% 이상인 산사태 고위험 구간이 다소 존재하는 것으로 나타났다. 특히 구덕산 지역의 경우 비교적 넓은 범위에서 산사태 발생 가능성이 높은 것으로 나타났으며, 백양산, 황령산 및 장산 지역의 경우 일부 국지적으로 산사태 발생가능성이 높은 구간이 존재하는 것으로 나타났다. 본 연구에서 작성된 산사태 예측지도는 부산지역의 산사태 재해저감 및 방재대책 수립을 위한 기초자료로 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대한다.
-
Development of a Landslide Susceptibility Map for Natural Slopes in the Busan Area Using Logistic Regression Model
-
Research Article
-
Evaluation of Dynamic Stability of Slopes Using 1g Shaking Table Tests and Finite Element Analysis
1g 진동대 실험과 유한요소해석을 통한 사면의 동적 안전성 평가
-
Minseo Moon, Geonju Park, Sugeun Jeong, Daehyeon Kim
문민서, 박건주, 정수근, 김대현
- Approximately 70% of South Korea’s land area consists of mountainous regions, and public awareness of seismic hazards has significantly increased following the …
우리나라 국토의 약 70%는 산지로 구성되어 있으며, 최근 경주 및 포항 지역에서 발생한 지진을 계기로 지진에 대한 사회적 경각심이 크게 고조되었다. 이러한 …
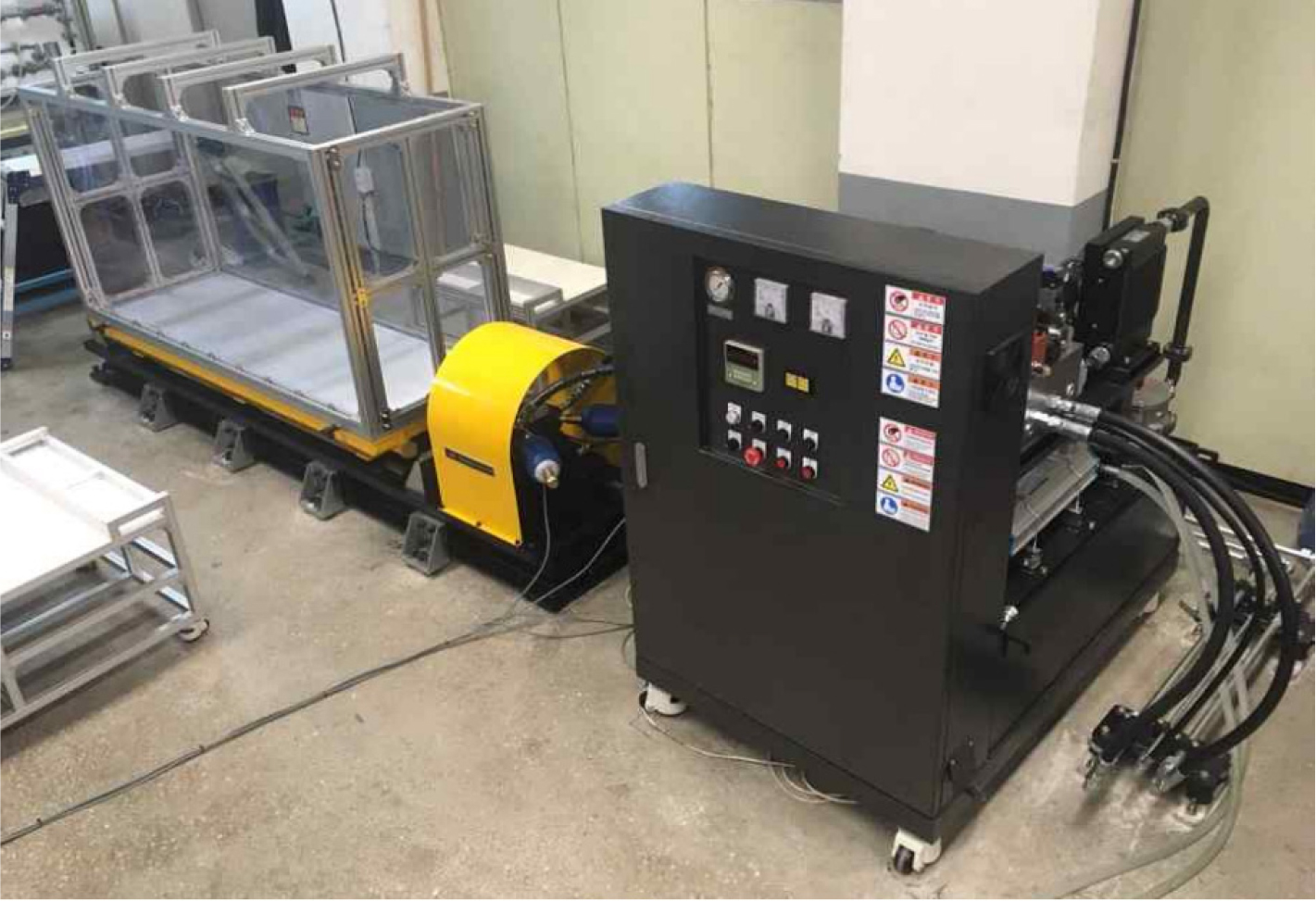
- Approximately 70% of South Korea’s land area consists of mountainous regions, and public awareness of seismic hazards has significantly increased following the 2016 Gyeongju and 2017 Pohang earthquakes. This study aims to quantitatively evaluate the dynamic stability of slopes under seismic loading by conducting 1g shaking table tests in parallel with finite element analysis. Laboratory model experiments were performed under various slope inclinations, and ABAQUS-based numerical models were developed under identical conditions. Time-history analysis was conducted to track the temporal variations in shear stress and shear strength, and the dynamic factor of safety (FS) was calculated along predefined slip surfaces. A comparison between experimental and numerical results verified the reliability of the numerical model. The proposed analysis method was found to effectively complement the limitations of pseudo-static analysis and contribute to more accurate seismic slope stability assessment.
- COLLAPSE
우리나라 국토의 약 70%는 산지로 구성되어 있으며, 최근 경주 및 포항 지역에서 발생한 지진을 계기로 지진에 대한 사회적 경각심이 크게 고조되었다. 이러한 배경 속에서, 지진 시 사면의 안정성 확보는 인명과 재산을 보호하기 위한 핵심 과제로 인식되고 있다. 본 연구는 지진하중에 따른 사면의 동적 안정성을 정량적으로 평가하기 위해, 1g 진동대 실험과 유한요소해석(Finite Element Analysis)을 병행하여 수행하였다. 다양한 경사 조건(1:2.0, 1:1.8, 1:1.3)을 고려하여 실내 모형실험을 수행하였고, 동일한 지반조건 및 경계조건을 반영하여 ABAQUS 기반의 수치해석 모델을 구축하였다. 이후 시간-이력 응답해석을 통해 사전에 정의된 가상 파괴면 상에서의 응력 성분을 추출하고, Mohr-Coulomb 기준에 따라 시간별 전단응력 및 전단강도를 산정하여 동적 안전율을 계산하였다. 해석 결과, 지진 입력의 주요 에너지가 작용하는 시점에서 FS가 급격히 저하되는 현상이 나타났으며, 이는 사면의 동적 취약 구간을 식별하는 데 효과적인 지표로 작용함을 확인하였다. 본 해석기법은 유사정적해석의 한계를 보완하고 정밀한 내진 안정성 평가에 기여 가능성을 확인하였다.

-
Evaluation of Dynamic Stability of Slopes Using 1g Shaking Table Tests and Finite Element Analysis
-
Research Article
-
Evaluation of Physical and Mechanical Properties of Synthetic Caprock Simulating the Mineral Composition of Caprock in Pohang and Janggi Basins, Korea
포항·장기분지 덮개암의 광물 조성을 모사한 인공 덮개암 제작 및 물리·역학적 특성 평가
-
Junyeong Seo, Hangseok Choi, Sangyeong Park, Kiseok Kim, Hyeontae Park
서준영, 최항석, 박상영, 김기석, 박현태
- In carbon capture and storage (CCS), maintaining caprock integrity is a critical factor for ensuring the long-term containment of CO2. …
이산화탄소 지중저장(Carbon Capture and Storage, CCS) 기술에서 이산화탄소를 심부지층에 장기간 안전하게 저장하기 위해서는 덮개암의 건전성이 필수적으로 확보되어야 한다. 일반적으로 덮개암 건전성 평가는 …
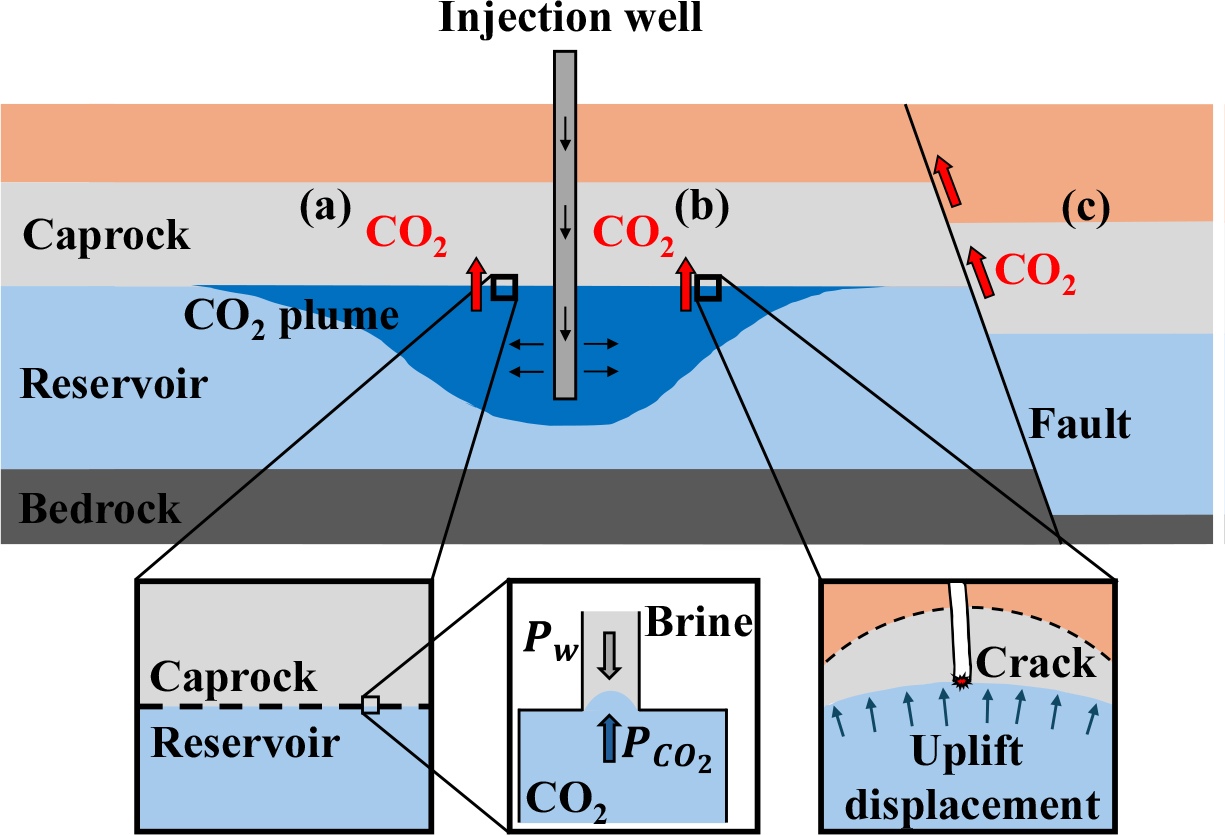
- In carbon capture and storage (CCS), maintaining caprock integrity is a critical factor for ensuring the long-term containment of CO2. Caprock integrity is typically assessed by analyzing the physical and mechanical properties of natural core samples obtained through drilling. However, due to the high costs associated with drilling and the risk of core damage, recent studies have increasingly explored the use of synthetic rock as an alternative. In this study, synthetic caprock samples were fabricated to replicate the mineral compositions of caprock from the Pohang and Janggi basins, which are considered potential CO2 storage sites in Korea. Porosity, permeability, and uniaxial compressive strength (UCS) were measured to evaluate the physical and mechanical behavior of the synthetic caprock under varying consolidation stress conditions. With increasing consolidation stress, porosity and permeability decreased, while UCS increased in both synthetic samples. However, notable differences in physical and mechanical properties were observed between the synthetic samples and natural rock, primarily due to the absence of chemical diagenetic processes, such as cementation and chemical compaction, in laboratory conditions. These findings provide essential baseline data for the fabrication of site-specific synthetic caprock analogs in CCS demonstration projects.
- COLLAPSE
이산화탄소 지중저장(Carbon Capture and Storage, CCS) 기술에서 이산화탄소를 심부지층에 장기간 안전하게 저장하기 위해서는 덮개암의 건전성이 필수적으로 확보되어야 한다. 일반적으로 덮개암 건전성 평가는 시추를 통해 채취한 자연암석 코어의 물리·역학적 특성을 분석하여 수행된다. 그러나 시추 비용이 높고 시료 손상의 우려가 있어, 최근에는 인공암석을 활용한 연구가 활발히 이루어지고 있다. 본 연구에서는 국내 이산화탄소 지중저장소 후보지로 평가되는 포항분지와 장기분지 덮개암의 광물 조성을 바탕으로 인공 덮개암을 제작하였다. 또한, 압밀 하중에 따른 인공 덮개암의 물리·역학적 특성을 평가하기 위해 공극률과 투수계수, 일축압축강도를 측정하였다. 실험 결과, 압밀 하중이 증가함에 따라 포항분지 및 장기분지 시료 모두 공극률과 투수계수는 감소하고, 일축압축강도는 증가하는 경향을 보였다. 그러나 두 시료는 자연암석과 비교할 때 물리·역학적 특성에서 차이를 보였으며, 이는 교결작용 및 화학적 압축과 같은 화학적 속성 작용이 실험실 조건에서 재현되지 않았기 때문으로 판단된다. 본 연구의 결과는 향후 국내 이산화탄소 지중저장 실증 사업에서 부지 특성을 반영한 인공 덮개암 제작을 위한 기초 자료로 활용될 수 있을 것이다.
-
Evaluation of Physical and Mechanical Properties of Synthetic Caprock Simulating the Mineral Composition of Caprock in Pohang and Janggi Basins, Korea
-
Research Article
-
Analysis of Frozen Ground Displacement Using SAR Interferometry
SAR 간섭기법을 활용한 동결 지반 변위 분석 연구
-
Sewon Kim, Hyun-Jun Choi, Hyangsun Han, YoungSeok Kim
김세원, 최현준, 한향선, 김영석
- Regions located in high latitudes or subject to large seasonal temperature variations often experience diverse geotechnical issues such as ground heave due …
고위도 지역이나 계절별 온도차가 큰 지역에서는 지반 결빙으로 인한 융기, 동결토 융해에 따른 침하, 반복적인 동결·융해로 인한 강도 저하, 그리고 지속 하중에 …
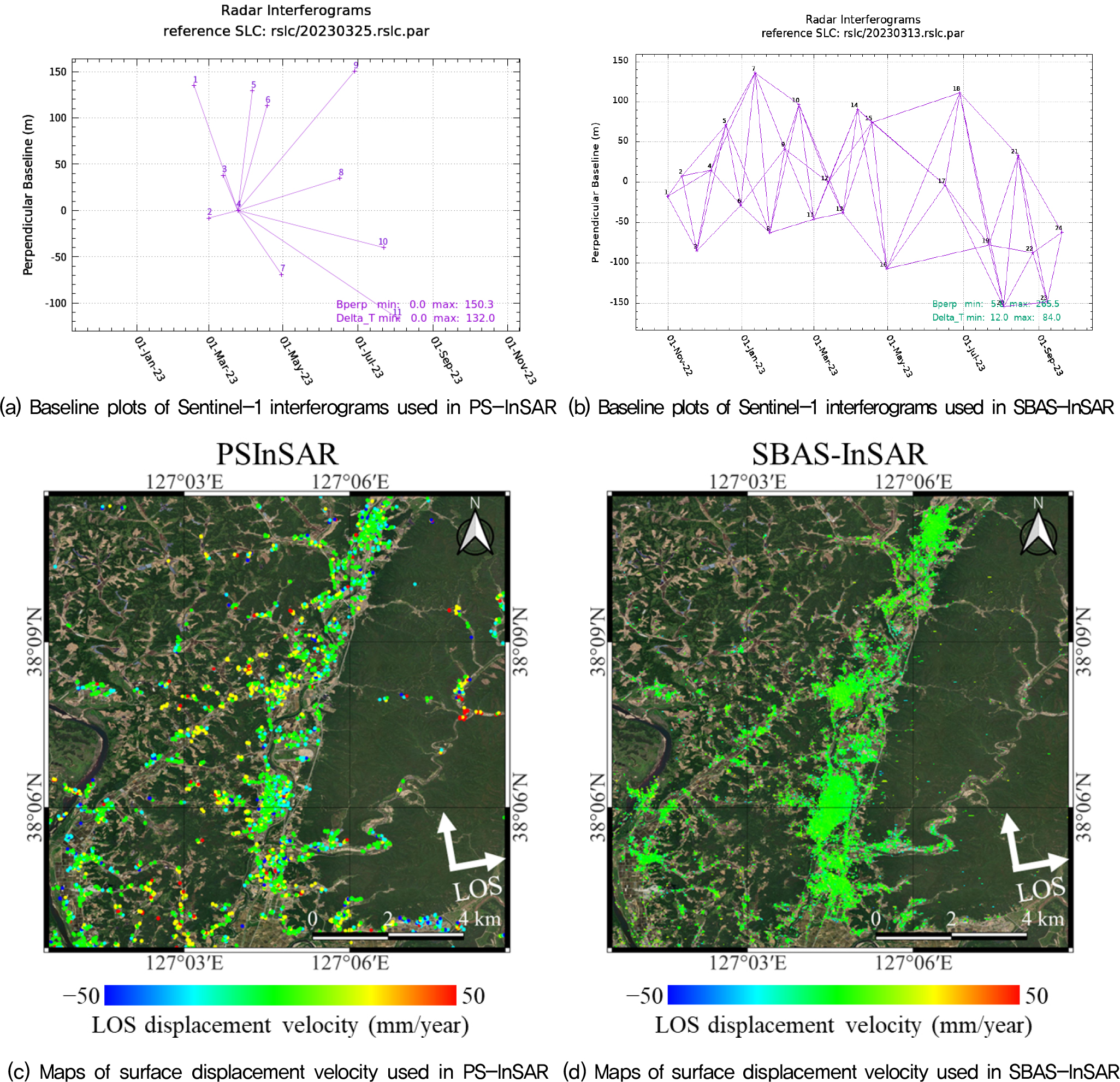
- Regions located in high latitudes or subject to large seasonal temperature variations often experience diverse geotechnical issues such as ground heave due to frost action, settlement caused by thawing, strength degradation from repeated freeze–thaw cycles, and creep deformation under sustained loads. Accurate monitoring of ground displacement is therefore essential for energy exploitation, resource development, and construction activities in such extreme environments. In this study, artificial frozen ground was prepared, and seasonal surface displacements were measured. These measurements were compared with time-series ground displacement derived from Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data using the Permanent Scatterer Interferometric SAR (PS–InSAR) technique. The results showed that when the annual maximum–minimum temperature difference reached approximately 40℃, the simulated frozen ground exhibited surface displacements of about 20mm. Furthermore, the InSAR–derived displacements demonstrated high consistency with the field measurements, thereby validating the accuracy of satellite–based SAR interferometric techniques for monitoring frozen ground displacement.
- COLLAPSE
고위도 지역이나 계절별 온도차가 큰 지역에서는 지반 결빙으로 인한 융기, 동결토 융해에 따른 침하, 반복적인 동결·융해로 인한 강도 저하, 그리고 지속 하중에 따른 크리프 현상 등 다양한 지반 문제가 빈번하게 발생한다. 이러한 극한 환경에서 에너지 및 자원 개발과 건설 활동을 수행하기 위해서는 지반 변위를 정밀하게 모니터링하는 것이 필수적이다. 본 논문에서는 모사된 동결 지반을 대상으로 계절별 지표 변위를 계측하고, 이를 Sentinel-1 위성으로부터 획득한 영상레이더(Synthetic Aperture Radar, SAR) 자료에 고정산란체 간섭 기법(Permanent Scatterer InSAR, PS-InSAR)을 적용하여 산출된 시계열 변위와 비교·분석하였다. 연구 결과, 연간 최대·최소 기온 차가 약 40℃에 이르는 조건에서 모사 지반의 지표 변위는 약 20mm 발생하였으며, 위성 기반 InSAR 분석값과 현장 계측 결과가 높은 상관성을 보였다. 이를 통해 위성 SAR 간섭 기법이 동결 지반 변위 모니터링에서 높은 정확성과 활용 가능성을 갖는다는 점을 확인하였다.
-
Analysis of Frozen Ground Displacement Using SAR Interferometry
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Geosynthetics Society
Journal of the Korean Geosynthetics Society
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Geosynthetics Society
Journal of the Korean Geosynthetics Society











