-
Research Article
-
Experimental Study on the Influence of Oil Contaminant Spill Location for Performance of Reactive Liner
유류 오염물 누출 위치가 반응성 라이너의 오염물 차단 성능에 미치는 영향에 관한 실험적 연구
-
Jaesub Lee, Jai-Young Lee, Kicheol Lee, Jeongjun Park, Gigwon Hong
이재섭, 이재영, 이기철, 박정준, 홍기권
- This study describes the results of model experiments to evaluate the oil diffusion barrier performance of a reactive liner containing 100% polynorbornene, …
본 연구에서는 100%의 폴리노보넨이 적용된 반응성 라이너에 대하여 유류 오염물의 누출이 발생한 위치에 따라 반응성 라이너의 유류 확산 차단 성능을 평가하기 위한 …
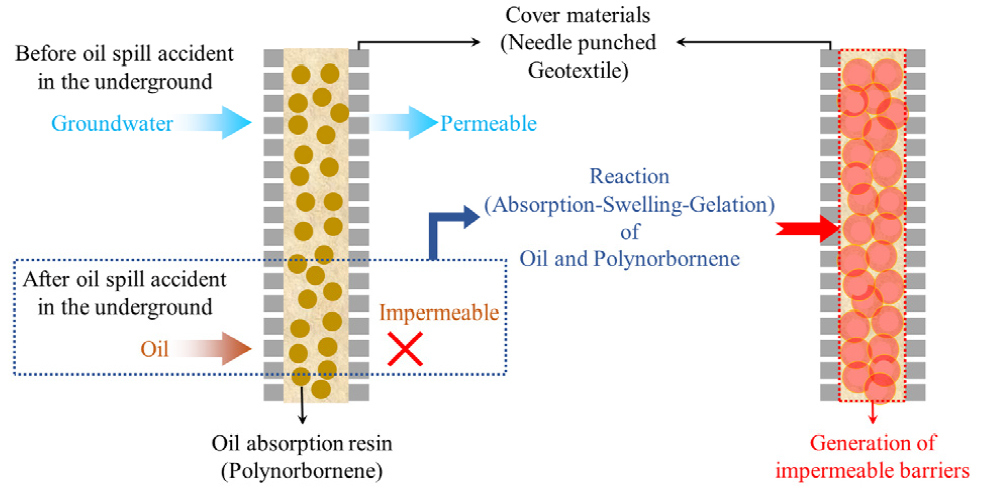
- This study describes the results of model experiments to evaluate the oil diffusion barrier performance of a reactive liner containing 100% polynorbornene, depending on the location of the oil spill. Model experiments showed that the reactive liner became impermeable after 8 hours in standard sand soil and achieved full barrier performance after approximately 48 hours, when TPH leaked from the reactive liner at a distance of 0.85D. However, in fine-grained soil, impermeability and barrier performance were achieved after approximately 6 hours and 24 hours, respectively. the reactive liner became impermeable and achieved barrier performance before approximately 7 hours and 10 hours in standard sand soil, and before approximately 4 hours and 10 hours in fine-grained soil, when TPH leaked from the reactive liner at a distance of 0.50D. Therefore, it was analyzed that the evaluation of groundwater flow rate needs to be reflected in the design of underground installation of reactive liners, as the influence of groundwater flow on the blocking performance of reactive liners due to oil diffusion differs depending on the ground conditions.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 100%의 폴리노보넨이 적용된 반응성 라이너에 대하여 유류 오염물의 누출이 발생한 위치에 따라 반응성 라이너의 유류 확산 차단 성능을 평가하기 위한 모형실험을 실시하였다. 모형실험 결과, 반응성 라이너로부터 0.85D 위치에서 TPH가 누출된 경우, 표준사 지반에서는 8H 경과 시에 반응성 라이너가 불투수성으로 변화되고, 약 48H가 경과되어야 완전한 차단 성능을 발휘하였다. 그러나 세립토 함유 지반에서는 약 6H 및 24H 경과 시에 각각 불투수성 변화 및 차단성능이 확보되었다. 반응성 라이너로부터 0.50D 위치에서 TPH가 누출된 경우, 표준사 지반에서는 약 7H 및 10H, 세립토 함유 지반에서는 약 4H 및 10H 이전에 반응성 라이너가 각각 불투수성 변화 및 차단 성능을 발휘하는 것을 알 수 있었다. 지반 조건에 따른 지하수 유동이 유류 확산에 기인한 반응성 라이너의 차단 성능에 미치는 영향이 다르기 때문에, 반응성 라이너의 지중 설치에 관한 설계 시 지하수 유속에 관한 평가가 반영될 필요가 있는 것으로 분석되었다.
-
Experimental Study on the Influence of Oil Contaminant Spill Location for Performance of Reactive Liner
-
Research Article
-
Proposal of a Predictive Algorithm for the Dry Unit Weight of Sandy Soils under Subzero Conditions
영하 온도 조건에서 사질토의 건조단위중량 예측 알고리즘 제안
-
Jaesub Lee, Gigwon Hong, Kicheol Lee
이재섭, 홍기권, 이기철
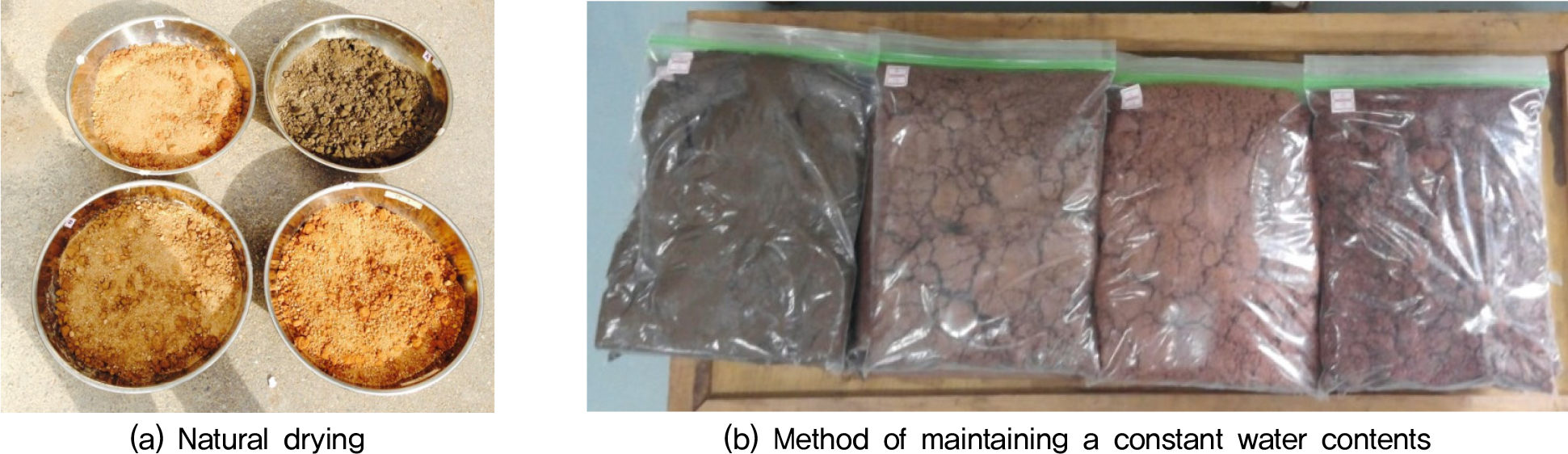
- This study experimentally demonstrates that the compaction behavior of sandy soils under sub-zero temperatures differs qualitatively from that at room temperature, and …
본 연구는 영하 조건에서 사질토의 다짐거동이 상온과 질적으로 달라지는 현상을 실험적으로 규명하고, 현장 입력값(온도 및 함수비)만으로 건조단위중량을 추정할 수 있는 머신러닝 알고리즘을 …
- This study experimentally demonstrates that the compaction behavior of sandy soils under sub-zero temperatures differs qualitatively from that at room temperature, and proposes a machine learning algorithm that predicts dry unit weight using only field input parameters(temperature and water content). For this purpose, standard compaction tests were conducted on four distinct sandy soils sampled from Songdo, Incheon, at laboratory temperature (20°C) and at sub-zero temperatures (0, -5, -10, -20°C). At zero-above temperature, the water content–density relationship exhibited a parabolic curve with a maximum dry unit weight at the optimal water content (OWC); under sub-zero conditions, however, the curve transitioned to a monotonically decreasing form toward the wet side. Based on these observations, Gradient Boosting Regressor were developed that inputs baseline compaction characteristics at zero above temperature and basic index properties, augmented with site temperature and water content, to output the dry unit weight for field conditions. Cross-validation showed strong agreement between predictions and measurements, with a coefficient of determination (R2=0.9587) and no systematic bias across the range. Accordingly, the proposed algorithm can provide immediate, realistic estimates of dry unit weight in winter even when an OWC peak is not observed, making it practical for cold-weather quality control.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 영하 조건에서 사질토의 다짐거동이 상온과 질적으로 달라지는 현상을 실험적으로 규명하고, 현장 입력값(온도 및 함수비)만으로 건조단위중량을 추정할 수 있는 머신러닝 알고리즘을 제안한다. 이를 위해 인천 송도에서 채취한 서로 다른 4종의 사질토에 대하여 상온(20°C)과 영하(0, −5, −10, −20°C)에서 표준 다짐시험을 수행하였다. 상온에서는 함수비 증가에 따라 최적 함수비에서 최대 건조단위중량을 보이는 포물선형 곡선이 관찰되었으나, 영하 온도에서는 습윤측으로 갈수록 건조단위중량이 지속적으로 감소하는 하향형 곡선으로 전환되었다. 이를 바탕으로, 상온 기준 다짐 특성과 기본 물성을 입력하고, 현장 온도와 함수비를 추가하여 현장의 건조단위중량을 출력 할 수 있는 Gradient Boosting Regressor 모델을 구축하였다. 교차검증 결과, 예측 및 실측값의 결정계수(R2)은 0.9587로 전 구간에서 편향 없이 양호한 적합도를 보였다. 따라서, 제안된 알고리즘은 최적 함수비가 관측되지 않는 영하 조건에서도 현재 현장의 조건만으로 현실적인 건조단위중량을 즉시 산정할 수 있어 동절기 품질관리에 실용적일 것으로 판단된다.국문초록

-
Proposal of a Predictive Algorithm for the Dry Unit Weight of Sandy Soils under Subzero Conditions
-
Research Article
-
A Study on a Computer Vision-Based Low-Cost Predictive Model for Bridge Safety Monitoring
컴퓨터 비전을 활용한 저비용 교량 안전관리 모니터링 예측 모델 연구
-
Taewon Park, Seunggil Jeong, Song Choi, Seong-Lim Lee, Bongjun Ji
박태원, 정승길, 최송, 이성림, 지봉준
- The aging of critical social infrastructure, including bridges, is a growing concern worldwide, necessitating long-term structural health monitoring and safety management. While …
교량을 비롯한 핵심 사회기반시설의 노후화는 전 세계적으로 심화되고 있으며, 이에 따른 구조 건전성의 장기적 모니터링 및 안전 관리의 필요성이 증대되고 있다. 기존의 …
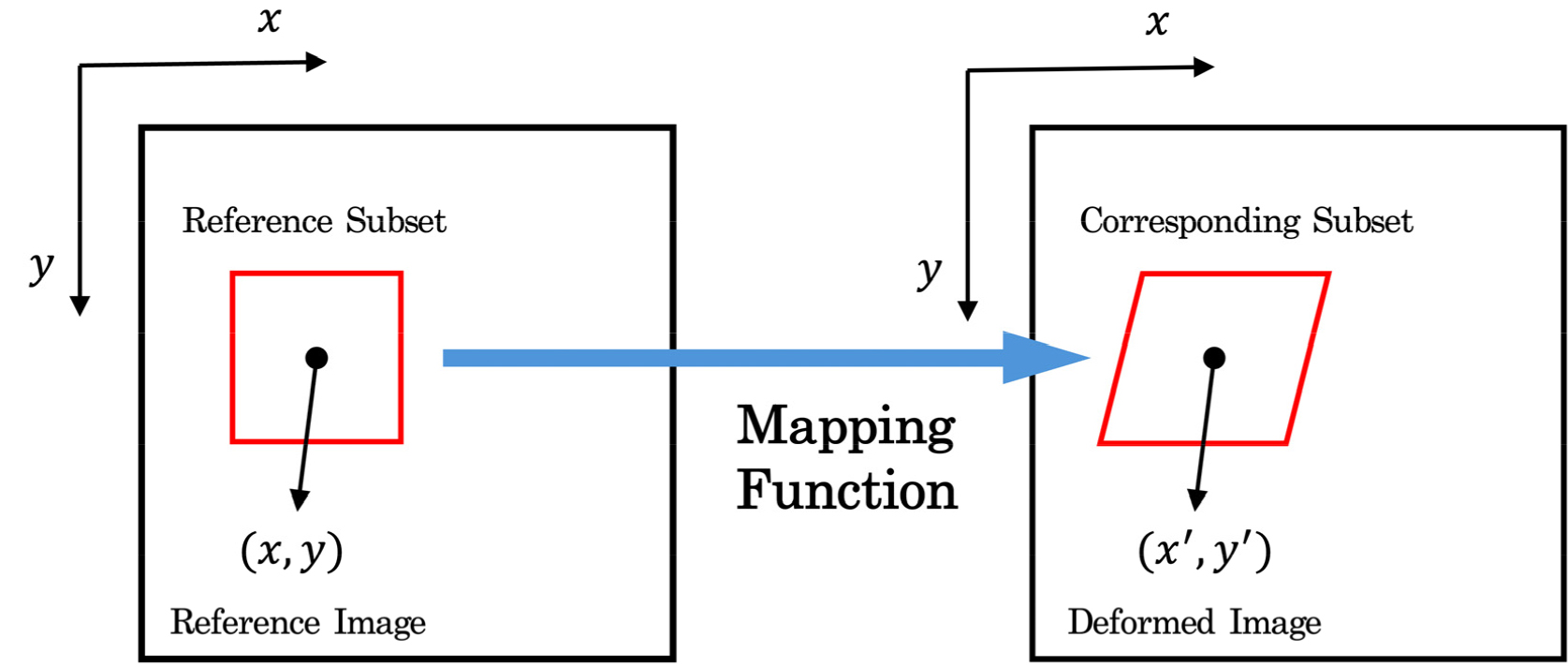
- The aging of critical social infrastructure, including bridges, is a growing concern worldwide, necessitating long-term structural health monitoring and safety management. While conventional methods utilizing contact-based sensors or unmanned aerial vehicles (drones) offer high accuracy, their widespread application is hindered by challenges such as high installation and maintenance costs, limitations to localized measurements, and constraints on long-term operation. To overcome these limitations, this study proposes a novel displacement monitoring methodology that leverages widely available CCTV infrastructure. The proposed technique extracts features from CCTV footage based on Digital Image Correlation (DIC) and converts them into time-series data. Subsequently, deep learning models such as Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) are applied to estimate the micro-displacements of the bridge. The performance of the proposed methodology was validated using video footage acquired from an actual bridge. The results confirmed a very low error, with a Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of 0.1116mm, when compared to the actual displacement data measured by contact-based displacement sensors. This research holds significant academic and practical value as it complements the technical and economic shortcomings of existing monitoring methods and presents a new direction for proactively utilizing CCTV infrastructure, an already established societal asset, for bridge safety management.
- COLLAPSE
교량을 비롯한 핵심 사회기반시설의 노후화는 전 세계적으로 심화되고 있으며, 이에 따른 구조 건전성의 장기적 모니터링 및 안전 관리의 필요성이 증대되고 있다. 기존의 접촉식 센서 기반 계측이나 무인항공기(드론)를 활용하는 방식은 높은 정확도를 제공하지만, 설치 및 유지관리 비용, 국소 계측의 한계, 그리고 장기간 운용의 제약으로 인해 광범위한 적용에 어려움이 존재한다. 본 연구에서는 이러한 한계를 극복하기 위한 대안으로, 광범위하게 보급된 CCTV 인프라를 활용하는 새로운 변위 모니터링 방법론을 제안한다. 제안된 기법은 CCTV 영상에서 디지털 이미지 상관법(Digital Image Correlation) 기반의 특징(Feature)을 추출하고, 이를 시계열 데이터로 변환한 후, Long Short-Term Memory(LSTM) 및 Gated Recurrent Unit(GRU)과 같은 딥러닝 모델을 적용하여 교량의 미소 변위를 추정한다. 실제 교량에서 취득한 영상을 대상으로 제안된 방법론의 성능을 검증한 결과, 접촉식 변위계로 측정한 실제 변위 데이터와 RMSE 기준 0.1116mm 의 매우 적은 오차를 보이는것을 확인하였다. 본 연구는 기존 모니터링 방식의 기술적, 경제적 단점을 보완하고, 이미 구축된 사회적 자산인 CCTV 인프라를 교량 안전 관리에 적극적으로 활용할 수 있는 새로운 방향을 제시한다는 점에서 학술적, 실용적 의의를 가진다.
-
A Study on a Computer Vision-Based Low-Cost Predictive Model for Bridge Safety Monitoring
-
Research Article
-
A Study on the Chemical Composition of Industrial by-Products from Different Sources
산업부산물 발생처에 따른 화학성분 조사 연구
-
Kwang-Wu Lee, Jae-Hyun Park, Se-Gwan Seo, Kyung-Ju Mun
이광우, 박재현, 서세관, 문경주
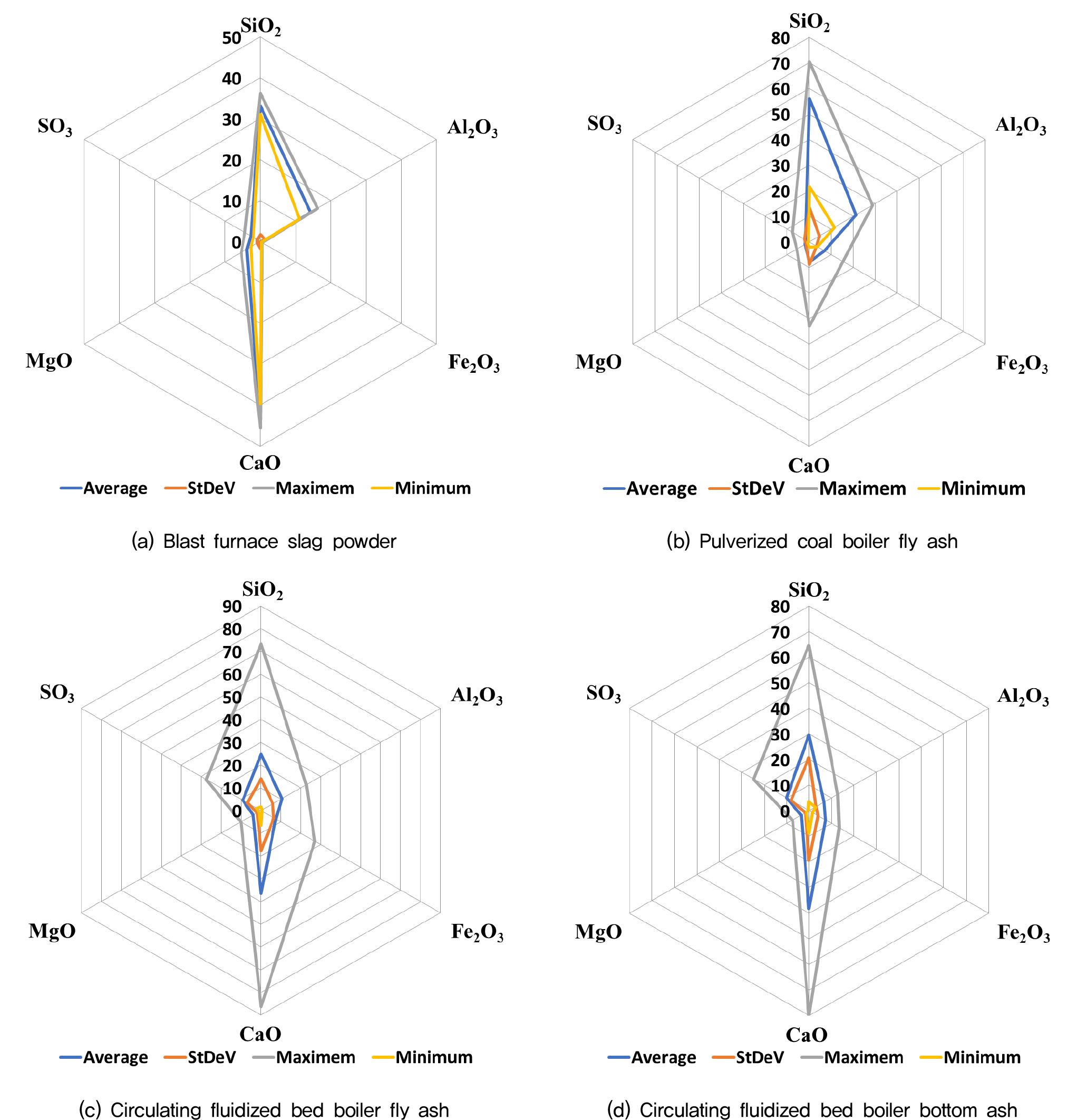
- This study analyzed the chemical composition of various industrial by-products according to their source. Chemical composition analysis of pulverized coal (PC) boiler …
본 연구에서는 다양한 산업부산물에 대해 발생처에 따른 화학성분을 분석하고 그 활용방안을 검토하였다. 미분탄 보일러 플라이애시에 대한 화학성분 분석 결과, 주요 화학성분 함량이 …
- This study analyzed the chemical composition of various industrial by-products according to their source. Chemical composition analysis of pulverized coal (PC) boiler fly ash revealed that the major chemical components generally comply with KS L 5405, making it suitable for use as a cement admixture. However, some sources did not comply with KS L 5405, necessitating selective application. Circulating fluidized bed combustion (CFBC) boiler ash generally does not comply with KS L 5405 in chemical composition and varies significantly depending on the source. Therefore, to effectively utilize CFBC ash, a continuous chemical composition analysis by source and time of generation is necessary to select usable materials. Furthermore, since the performance level required for inorganic binders in the field of geotechnical engineering field is lower than that of general cement or concrete, it is expected that CFBC ash can be selectively utilized as an inorganic binder admixture or aggregate substitute for ground improvement and reinforcement.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 다양한 산업부산물에 대해 발생처에 따른 화학성분을 분석하고 그 활용방안을 검토하였다. 미분탄 보일러 플라이애시에 대한 화학성분 분석 결과, 주요 화학성분 함량이 대체로 KS L 5405에 부합하여 시멘트 혼화재로 활용이 가능하나, 일부 발생처의 경우에는 KS L 5405에 부합하지 않는 것으로 분석되어 선별 적용이 필요한 것으로 조사되었다. 이에 반해, 순환유동층(CFBC) 보일러 연소재는 화학성분 조성이 대체로 KS L 5405에 부합하지 않고, 발생처에 따라서도 크게 차이를 보인다. 따라서 CFBC 연소재의 유효활용을 위해서는 발생처 및 발생시기에 따른 화학성분 분석을 지속적으로 실시하여 활용 가능한 재료를 선별할 필요가 있다. 또한 CFBC 연소재는 품질 편차가 크고 유해물질 기준과 수경성 확보가 어려워 대부분 매립 또는 소각처리 되고 있다. 그러나, 지반분야는 무기결합재의 요구 성능 수준이 일반적인 시멘트나 콘크리트에 비해 작고 유동적이기 때문에, CFBC 연소재도 지반 개량 및 보강 용도의 무기결합재 원료나 골재 대체재료로 선별적으로 활용이 가능할 것으로 판단된다.
-
A Study on the Chemical Composition of Industrial by-Products from Different Sources
-
Research Article
-
A Study on the Predictive Model for Estimating the Productivity of Vibratory Rippers Based on Rock Strength
진동 리퍼의 생산량 추정을 위한 암반강도에 따른 생산량 예측 모델 고찰
-
Mingyu Kim, Chulho Lee
김민규, 이철호
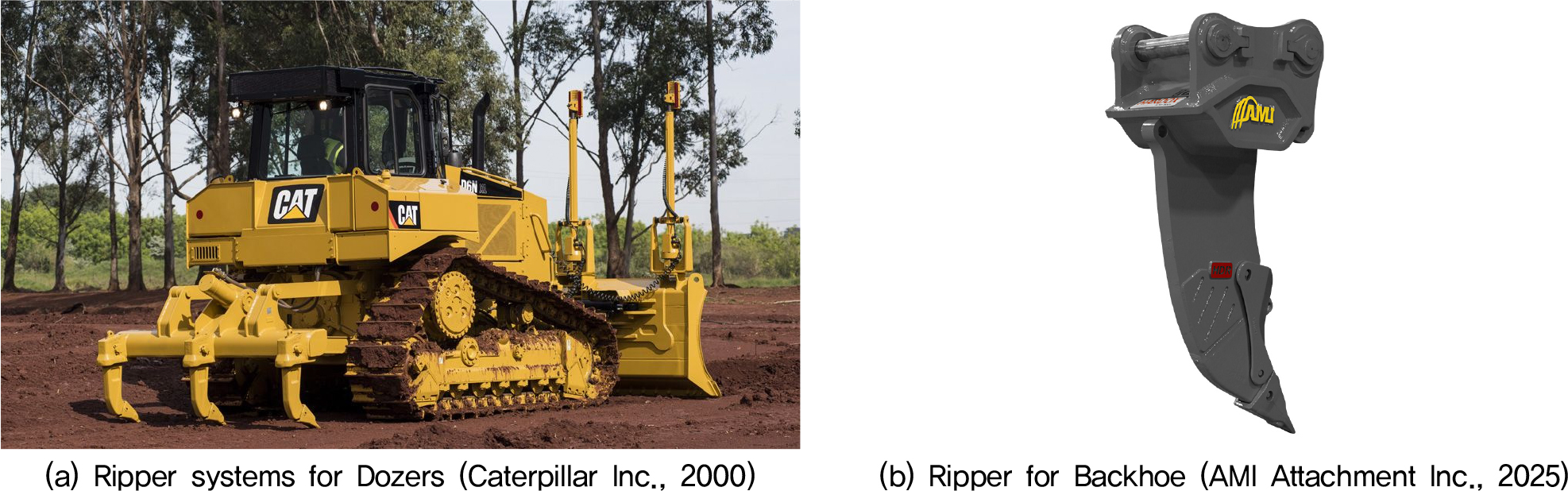
- This study presents a predictive model to estimate the productivity of excavator-mounted vibratory rippers as a function of rock strength, with the …
진동 리퍼의 현장 적용성을 높이기 위해, 본 연구에서는 굴삭기용 진동 리퍼의 생산성을 암반 강도에 따라 예측할 수 있는 모델을 제안하였다. 기존의 리퍼 …
- This study presents a predictive model to estimate the productivity of excavator-mounted vibratory rippers as a function of rock strength, with the aim of improving their field applicability. Previous research on ripper productivity has predominantly focused on bulldozer-mounted rippers, while academic studies on excavator-mounted vibratory rippers remain scarce. To address this research gap, data provided by overseas manufacturers and field test results in this study were utilized to analyze the quantitative relationship between uniaxial compressive strength (UCS) of rock and the corresponding production rate. Various machine learning algorithms were compared, and the Gamma regression model was found to most effectively represent the exponential decrease characteristics associated with increasing rock strength. Furthermore, empirical equations originally developed for impact hammers were extended to derive RQD-based productivity curves, enabling the proposed model to be applied even at sites where RQD data are not available. Although the dataset used in this study is limited and may restrict generalization, the proposed approach provides a quantitative foundation for evaluating and predicting the productivity of backhoe-mounted vibratory rippers. Future work will focus on improving model reliability and prediction accuracy through the integration of additional domestic field data.
- COLLAPSE
진동 리퍼의 현장 적용성을 높이기 위해, 본 연구에서는 굴삭기용 진동 리퍼의 생산성을 암반 강도에 따라 예측할 수 있는 모델을 제안하였다. 기존의 리퍼 생산성 관련 연구는 대부분 도저용 리퍼에 한정되어 수행되었으며, 굴삭기용 진동 리퍼에 관한 학술적 연구는 매우 제한적이다. 이에 본 연구에서는 해외 제조사 제공 자료와 현장 시험 결과를 활용하여, 진동 리퍼의 생산성을 암반의 일축압축강도와 생산량 간의 상관관계로 정량적으로 분석하였다. 상관관계 분석에는 다양한 머신러닝 기법을 적용하였으며, 그중 감마 회귀(Gamma Regression) 방식이 암반 강도 증가에 따른 생산량의 지수적 감소 특성을 가장 안정적으로 반영하는 것으로 나타났다. 또한, 기존 문헌에서 제시한 임팩트 해머의 경험식을 확장 적용하여 RQD별 생산량 곡선을 제시함으로써, RQD 지표가 확보되지 않은 현장에서도 활용 가능한 예측 모델을 구축하였다. 비록 데이터의 양이 제한적이며 일반화에는 한계가 있으나, 본 연구는 굴삭기용 진동 리퍼의 생산성을 정량적으로 평가하고 예측할 수 있는 기초적 근거를 제시한다는 점에서 의의가 있다. 향후에는 국내 현장 데이터를 추가 확보함으로써 모델의 신뢰성과 예측 정밀도를 향상시킬 예정이다.

-
A Study on the Predictive Model for Estimating the Productivity of Vibratory Rippers Based on Rock Strength
-
Research Article
-
Structural Characteristics and Behavioral Analysis of a Buffer Net Applied to Debris Flow Protection Facilities
토석류 방호시설 적용을 위한 충격 흡수형 네트의 구조적 특성 및 거동 분석
-
Jongju Kim, Chanyoung Park, Dabin Kwon, YoungSeok Kim, Seungjoo Lee, Yongseong Kim
김종주, 박찬영, 권다빈, 김영석, 이승주, 김용성
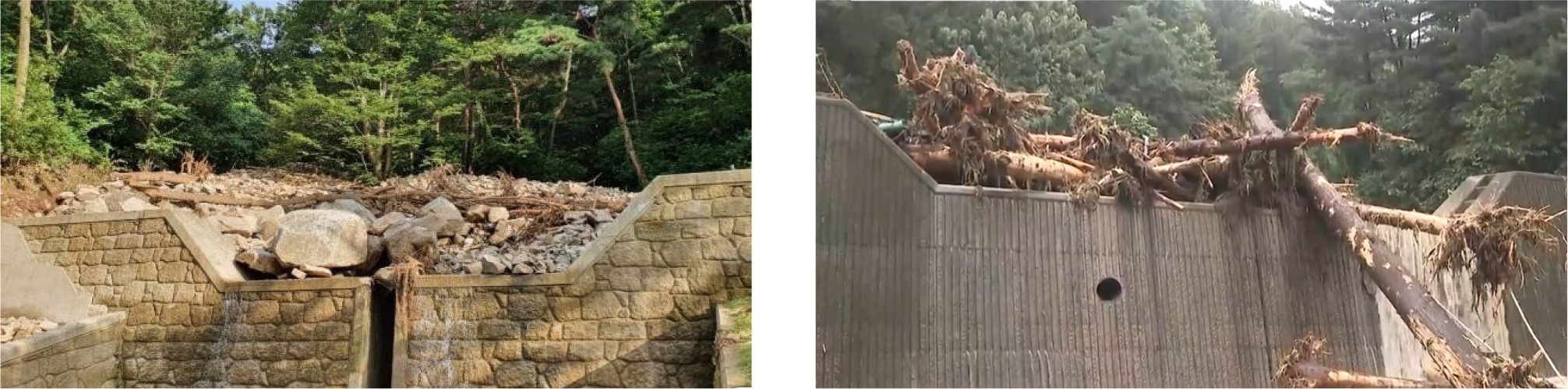
- This study aims to evaluate the impact mitigation performance of net structures applied to debris-flow protection facilities, as debris-flow damages have increased …
본 연구에서는 집중강우로 인한 토석류 피해 증가와 더불어 방호시설에 대한 필요성이 대두됨에 따라 토석류 방호시설에 주로 적용되는 네트 구조의 충격 저감 성능을 …
- This study aims to evaluate the impact mitigation performance of net structures applied to debris-flow protection facilities, as debris-flow damages have increased due to recent episodes of extreme rainfall and the demand for protective facilities has consequently grown. Tensile tests were conducted on 16-mm-diameter, 2.0m long wire ropes, comparing the energy absorption capacity of conventional wire ropes with that of buffer-type wire ropes combined with extension springs (spring diameter: 15mm, spring constant: 69.4kN/m). In addition, free-fall numerical simulations were performed using the Abaqus program to analyze the impact response of conventional nets and shock-absorbing nets. The tensile test results indicate that the buffer-type wire rope exhibits approximately 1.76times higher energy absorption per unit length than the conventional wire rope. The numerical analysis further revealed that, under identical impact conditions, the maximum tensile force acting on the shock-absorbing net was reduced to about 25% of that of the conventional net, while the impact duration increased by approximately 60%. Therefore, the shock-absorbing net is considered a more effective and safer alternative for debris-flow protection facilities compared to conventional net systems.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 집중강우로 인한 토석류 피해 증가와 더불어 방호시설에 대한 필요성이 대두됨에 따라 토석류 방호시설에 주로 적용되는 네트 구조의 충격 저감 성능을 평가하기 위해 직경 16mm, 길이 2.0m 와이어로프와 직경 15mm, 상수 69.4kN/m의 인장스프링이 결합한 완충형 와이어로프의 에너지 흡수 능력을 인장실험을 통해 비교 분석하였다. 인장실험 결과, 완충형 와이어로프의 단위 길이당 에너지 흡수량은 일반 와이어로프보다 약 1.76배 크게 나타났으며, 수치해석 결과 충격 흡수형 네트는 동일한 충격조건에서 최대 인장력이 일반 네트의 약 25% 수준으로 감소하고 작용 시간은 약 60% 증가하는것으로 나타났다. 따라서 충격 흡수형 네트는 토석류 방호시설에 적용할 경우 일반 네트에 비해 보다 높은 안전율을 확보할 수 있는 방호 대안으로 판단된다.
-
Structural Characteristics and Behavioral Analysis of a Buffer Net Applied to Debris Flow Protection Facilities
-
Research Article
-
A Study on the Engineering Properties of Mortar with Industrial by-Products for Ground Reinforcement
산업부산물 기반 무기결합재와 바텀애시를 활용한 지반보강 모르타르의 기초 성능 평가
-
Kwang-Wu Lee, Jae-Hyun Park, Se-Gwan Seo, Kyung-Ju Mun
이광우, 박재현, 서세관, 문경주
- An inorganic binder and mortar was developed for ground reinforcement based on industrial by-products, and its applicability was evaluated through laboratory and …
본 연구에서는 산업부산물 기반 무기결합재와 지반보강용 모르타르를 개발하였으며, 실내 및 현장 실험을 통해 그 활용성을 검토하였다. 산업부산물을 70% 적용한 무기결합재와 골재 대체재료로 …
- An inorganic binder and mortar was developed for ground reinforcement based on industrial by-products, and its applicability was evaluated through laboratory and field experiments. Laboratory mixing tests were conducted on the mortar containing 70% industrial by-products as the inorganic binder and circulating fluidized bed boiler bottom ash as an aggregate substitute. An optimal mixing design method according to field conditions and required strength levels was investigated and its applicability was evaluated through the field experiment. The proposed foundation method using industrial by-product-based mortar can install uniform columns by pre-boring and then injecting the high-strength mortar based on industrial by-products. Therefore, it is expected to be effectively utilized in applications such as structural foundations, embankment piles, and embankment reinforcement.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 산업부산물 기반 무기결합재와 지반보강용 모르타르를 개발하였으며, 실내 및 현장 실험을 통해 그 활용성을 검토하였다. 산업부산물을 70% 적용한 무기결합재와 골재 대체재료로 순환유동층보일러 바텀애시를 혼합한 모르타르에 대해 실내 배합시험을 수행하여, 현장 여건 및 요구강도수준에 따른 적정 배합설계 방안을 제시하였으며, 현장 시험시공을 통해 현장 적용성을 확인하였다. 본 연구에서 제시한 산업부산물 기반 모르타르를 적용한 기초공법은 선천공 실시 후 산업부산물 기반의 고강도 모르타르를 주입하여 균일한 단면의 개량체를 형성할 수 있어, 중저층 구조물기초, 성토지지말뚝, 하천제방 보강 등에 효과적으로 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
A Study on the Engineering Properties of Mortar with Industrial by-Products for Ground Reinforcement
-
Research Article
-
Assessment of the Applicability of a Net-Type Check Dam Equipped with an Early Warning Sensor System
조기경보용 센서 시스템이 적용된 네트형 사방댐의 적용성 평가
-
Jongju Kim, Chanyoung Park, Dabin Kwon, YoungSeok Kim, Seungjoo Lee, Yongseong Kim
김종주, 박찬영, 권다빈, 김영석, 이승주, 김용성
- This study was conducted to evaluate the practical applicability of an early warning sensor system for net-type check dams. A strain gauge …
본 연구는 네트형 사방댐에 적용 가능한 조기경보용 센서 시스템의 실효성을 확인하기 위해 수행되었다. 우면산 사방댐을 대상으로 네트 구조물의 와이어로프에 변형률계를 설치하였으며, 토석류 …
- This study was conducted to evaluate the practical applicability of an early warning sensor system for net-type check dams. A strain gauge was installed on the wire ropes of the net structure at the Umyeonsan check dam site, enabling real-time measurement of micro-displacements caused by debris-flow impacts. A monitoring system was established to transmit the measured data to a management server through an IoT-based communication network. Tensile tests were performed to verify the accuracy and reliability of the sensor, and field application results showed that even minor impacts were clearly detected, demonstrating the feasibility of real-time impact load monitoring. Based on the measured displacement and load data, the applicability of a multi-level warning system was examined, indicating that the proposed approach can enhance integrated response capabilities compared to conventional systems where protective structures and warning functions operate separately. This study provides fundamental data for introducing an early warning function to net-type check dams and is expected to contribute to improving initial response to debris-flow events.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 네트형 사방댐에 적용 가능한 조기경보용 센서 시스템의 실효성을 확인하기 위해 수행되었다. 우면산 사방댐을 대상으로 네트 구조물의 와이어로프에 변형률계를 설치하였으며, 토석류 충격에 따른 미소 변위를 실시간으로 측정하고 IoT 기반 통신망을 통해 관리 서버로 전송하는 모니터링 체계를 구축하였다. 인장실험을 통해 센서의 측정 정밀도와 신뢰도를 검증하였으며, 현장 적용 결과 작은 충격에도 변위 변화가 명확하게 계측되어 실시간 하중 모니터링이 가능함을 확인하였다. 또한 계측된 변위·하중값을 기반으로 단계별 경보 설정 가능성을 검토하여, 방호시설과 경보 체계가 분리되어 있던 기존 시스템 대비 통합 대응 기능을 강화할 수 있음을 제시하였다. 본 연구는 네트형 사방댐에 조기경보 기능을 도입하기 위한 기초자료를 제공하며, 향후 토석류 발생 초기 대응을 개선하는 데 활용될 수 있을 것으로 판단된다.

-
Assessment of the Applicability of a Net-Type Check Dam Equipped with an Early Warning Sensor System
-
Research Article
-
Evaluation of the Applicability of a Digital Twin-Based Stability Assessment Through Model Experiments
모형실험을 통한 디지털트윈 기반 안정성 평가의 적용성 검증
-
Wooseok Shin, Chungsik Yoo
신우석, 유충식
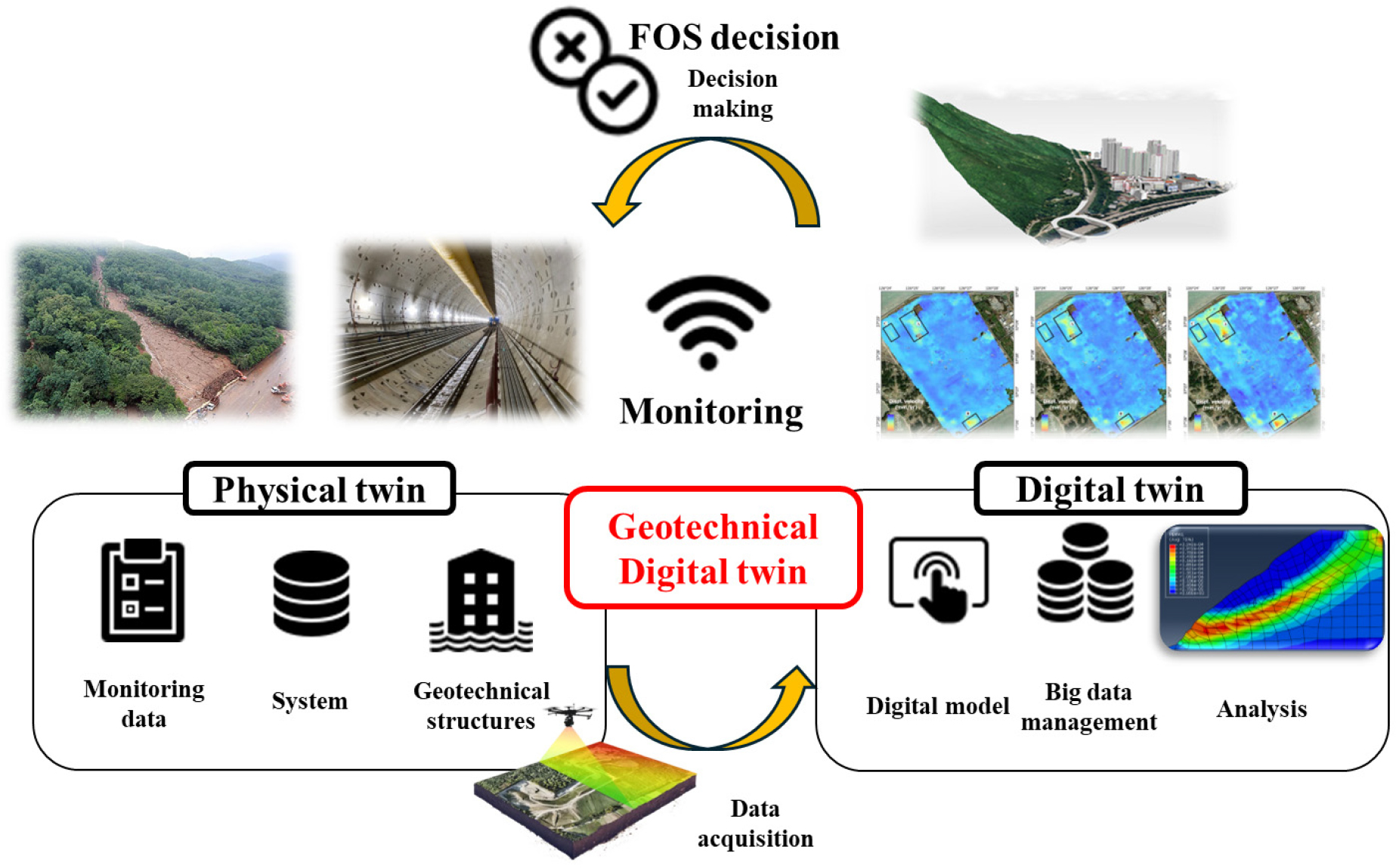
- Digital twin (DT) technology links physical structures with virtual models to reduce uncertainty and support prediction and decision-making, and recent applications have …
디지털트윈(DT)은 현실 구조물과 가상 모델을 연동하여 불확실성을 줄이고 예측 및 의사결정을 지원하는 기술로, 재료적 비균질성과 경계 조건의 불확실성이 큰 지반공학 분야에서도 적용 …
- Digital twin (DT) technology links physical structures with virtual models to reduce uncertainty and support prediction and decision-making, and recent applications have begun to emerge in geotechnical engineering, where material heterogeneity and uncertainties in boundary conditions are significant. This study proposes a DT-based stability assessment procedure to improve the consistency between stability analyses and measured responses of geotechnical structures, using laboratory model tests on a slope and a retaining wall as a preliminary step prior to field implementation. In the proposed framework, an initial finite element (FE) model is generated from iPad LiDAR scans of the model geometry, with point-cloud preprocessing carried out in CloudCompare and AutoCAD; incremental loading analyses are then performed in Abaqus, the elastic modulus E, internal friction angle φ, and cohesion c are automatically calibrated via a Python–Abaqus coupled Bayesian optimization scheme so that the computed horizontal displacements match those measured by digital image correlation (DIC) and laser displacement transducers, and finally shear strength reduction (SSR) analyses are conducted on the calibrated model to evaluate stage-wise factors of safety (FoS). In this way, a cyclic DT workflow that links experiment, analysis, calibration, and stability evaluation is established. The calibrated analyses showed good qualitative agreement with the DIC displacement fields and the measured horizontal displacements, and the FoS values obtained from SSR were comparable to those from limit equilibrium methods (LEM), confirming the validity of the proposed calibration–analysis procedure. These results demonstrate that the LiDAR-based and measurement-based calibration scheme can effectively reproduce the actual behavior of geotechnical structures and suggest its potential extension toward real-time monitoring and hazard-mitigation-oriented DT applications.
- COLLAPSE
디지털트윈(DT)은 현실 구조물과 가상 모델을 연동하여 불확실성을 줄이고 예측 및 의사결정을 지원하는 기술로, 재료적 비균질성과 경계 조건의 불확실성이 큰 지반공학 분야에서도 적용 사례가 점차 보고되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 지반 구조물의 안정성 해석과 실측 간 정합성 문제를 해결하고자, 실제 구조물 적용에 앞서 모형 사면 및 옹벽 실험을 대상으로 디지털트윈 기반 안정성 평가 절차를 제안하였다. 제안된 절차는 iPad LiDAR로 취득한 구조물 형상을 CloudCompare–AutoCAD 전처리를 통해 초기 유한요소 모델로 구축하고, 단계별 하중을 증가시키며 Abaqus에서 수치해석을 수행한 뒤, DIC 및 레이저 변위계로 계측된 수평변위와의 차이를 최소화하도록 Python–Abaqus 연동 베이지안 최적화를 통해 탄성계수( E), 내부마찰 각(𝜑), 점착력( c)을 자동 보정하고, 최종적으로 보정된 모델에 전단강도 저감법(Shear Strength Reduction, SSR)을 적용하여 단계별 안전율(FoS)을 평가하는 방식으로 구성된다. 이와 같이 실험–해석–보정–평가가 순환되는 디지털트윈 절차를 구현하였다. 그 결과, 보정 후 해석 결과는 DIC 변위장 및 실측 수평변위와 정성적으로 양호한 일치를 보였으며, SSR을 통한 안전율이 한계평형법(LEM) 결과와 유사하게 도출되어 보정–해석 절차의 타당성을 입증하였다. 본 연구는 LiDAR 기반 형상 데이터와 실험 계측을 연계한 보정 절차가 지반 구조물의 실제 거동을 효과적으로 재현할 수 있음을 확인하였으며, 향후 실시간 모니터링 및 재해 저감형 디지털트윈 기술로의 확장 가능성을 제시한다.
-
Evaluation of the Applicability of a Digital Twin-Based Stability Assessment Through Model Experiments
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Geosynthetics Society
Journal of the Korean Geosynthetics Society
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Geosynthetics Society
Journal of the Korean Geosynthetics Society











